Research Notes on Reinforcement Learning
Work in Process
Research Focus
I am currently working on few projects, including B(N)PO algorithm and related Replay Buffer enhancements w.r.t. Credit Assignment, GAHIL approach which aim to help in HRL, Meta-Learning and even in HER settings. However I am bit out of my schedule as I am not able to allocate as much timeslot towards those research directions as I would like. Though meanwhile I will at least sort of my work and document my current status in those areas bellow, and will follow up with updates as I will progress.
GAHIL - Generative Adversarial Hindsight Imitation Learning
In this research I was strongly inspired by GAIL paper, which use GANs to imitate expert trajectories in order to learn its own policy. Quite nice clean simplified implementation you can find here. And as I was working in HER settings in my previous projects, I get close to this idea of looking at problem. Where even if goal was not achieved by original interaction of policy with environment, states on achieved trajectory was taken and considered as goals for observed trajectories in future learning. And that closely reassembles expert trajectories whose GAIL trying to collect in order to imitate from! Therefore Generative Adversarial Hindsight Imitation Learning, and I see several existing algorithms which can potentialy benefit from this technique, as described bellow.
BlackBox
Real world does not provide well defined reward function, but we usually can get signal if we achieved our objective or not, if was some failure on the way and so on. It looks now pretty much like classic sparse HER settings, though in HER all the learning happens at self-play time, which is offline, but in real world we not necessary have function available to evaluate our self-play. I call this BlackBox environment. And for this kind of settings we can use GAHIL, which during interacting with environment, online time, learns reward function, and during self-play, offline time, we query GAHIL for actual rewards we use for learning our policy ( policy never see rewards from environment itself ). I train GAHIL in sparse fashion, where lets say achieved goals should output reward +1, and all others -1, and seems works well. I perform tests over reacher environment, where UnityML provide me reward function at time of interaction but no way to query it outside, therefore I implemented HER + GAHIL and test it versus original settings. And you can also check implementation of GAHIL here.
HRL
Idea of using GAHIL in context of HRL sparks when I come across HAC paper, multi level hierarchy to tackle Credit Assignment problem capable to compose at least up to 3 layers! For example, in Euclidean space we can train GAHIL by assigning rewards +1 for neighborhood states and GAHIL learns basically norm function, example of using GAHIL for reacher environment with static goal in described fashion you can check here :
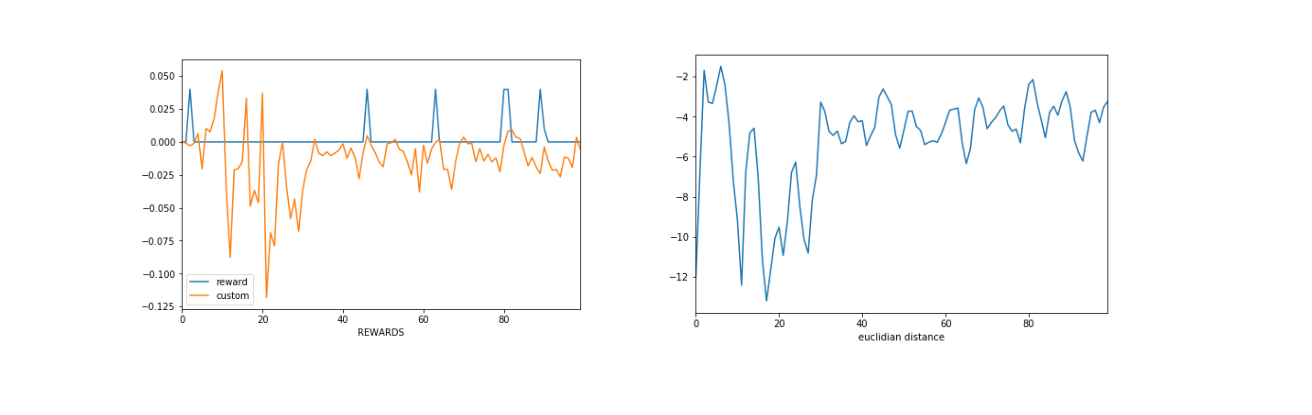
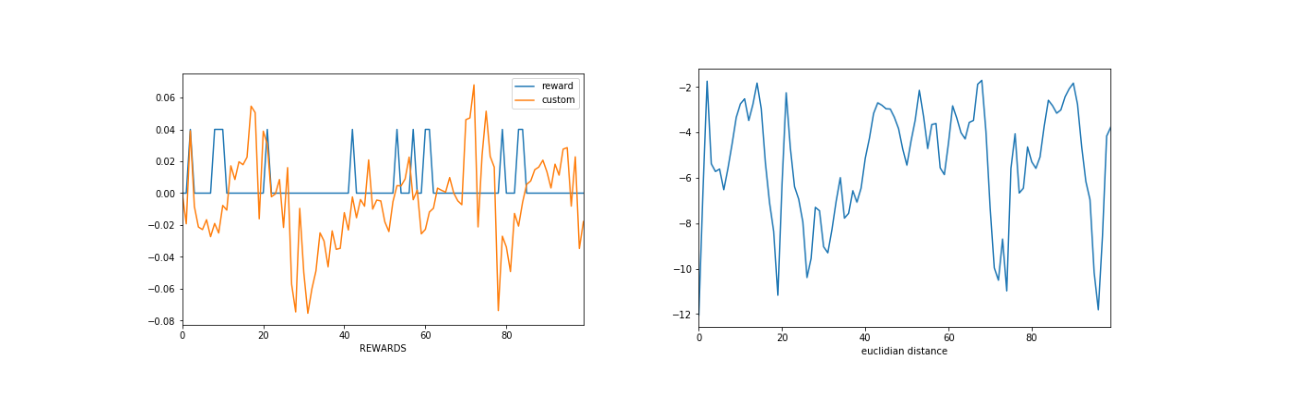
Therefore using GAHIL in HAC as second layer can potentially act as agent which tries to achieve goal in shortest path given norm of not Euclidean space but space of connected layer, if that make sense :) . I tried just few experiments on this yet, does not looks breath taking, but showing bit of potential behind :
Total accumulated reward is low, however trajectory is what we would like to be. Though if it is due GAHIL, or only last layer is the one responsible, that is not well evaluated.
For now GAHIL for HRL is idea which I think is worth to experiment with, but as for results on that front, well.. yet to be achieved.
Meta-Learning
Actually by this time I was planning to do more of research over meta-learning, but did not make it though. So here I have only brief ideas how GAHIL can be used here. Generally, in Meta-Learning we try to learn of several environments relatively concurrently, and try to learn policy to quickly adapt to new environments. What GAHIL can do here, is learn somehow universally reward signal for multiple environments, as we forwarding <state1, state2, action> to GAHIL where it can learn based on this transition in which environment we are and assign appropriate reward, also by addition to this triplet like transition, we forwarding goal, and can potentially forward reward from previous transition as well. Therefore we can have unified reward function across environments, which can reflect and signal similarities in state-action-goal between environments, what can possibly smooth learning for our policy. Interesting to note is that GAHIL should act as a SIGNAL not as a fully shaped reward function, and that I consider more ideal case when it come to learn RL policy on top of it.
Credit Assignment
One of the very important part of Reinforcement Learning to tackle is reward function and credit assignment over episode horizon. That’s being said, there are some tricky tasks, from simplest one MountainCar which requires to do counter intuitive steps to achieve goal, up to more complex robotic ones, like Fetch and Reach which require to encourage sequence of specific subtasks to achieve in order to meet goal of complex one, and of course Walker etc.
Engineering complex reward function by hand will force RL framework, neural nets in particular, to fit problem into engineer point of view, and this I consider both win situation and failure mode as well. Failure mode because we cutting freedom of RL to comes with its own independent solution, while trying to fit to our suggested one which is not necessary an optimal and RL will try to exploit potential mistakes when it consider it is more feasible to do so. On the other hand win situation, because considering fully automated systems, our hand engineered ideas can have edge per problem scenario over genaralised / optimized solutions.
But overall I prefer techniques which works with reward functions which are in form of signal, not the hand engineered. That is the reason why I keep more focused on HER, comes out with GAHIL or MROCS (applied at my recent projects). Same time I consider replay buffer one of the key behind learning effectively, including more extensive self-play which I will address in following sections.
Floating Step
This technique I introduced in one of my previous blog post, and is based on extension of k-step estimators. Main idea is reload episode from replay buffer and recalculate k-step over that episode with different k, which introduce more training signal ( instead of K step, we doing now 1…K steps ), and possibly allows HER to work in k-step setup naturally. This obviously comes with performance overhead but can be hacked around.
n-step GAE
As I empathized in previous blog post I consider GAE as quite efficient Credit Assignment approach. It naturaly extend reward as signal approach via potential-based shaping :
it basically adds to every step, which contains signal from reward function, also self-assigned value, which RL algorithm can callibrate itself (possibly including lambda as well!), therefore it can act as assigning credit, importance, per state! On the other side, GAE is designed originaly the way it goes trough full episode, which is logical as it suppose to re-evaluate credit for full episode and assign values to particular states based on that. However, when we look at reward function as signal only, then Q-value function should represent our ‘true’ value in particular state including last state which represent total reward achieved trough episode, not necessary sum of reward as those now i consider as signals only. In that way we can chop episode to the pieces and do GAE only at that piece of episode, where Q-values of starting state and end state of that piece of episode will be used in TD Error to compensate doing GAE solely over this piece of episode, achieving k-step estimate while preserving gradients for DDPG :
This can be tricky to implement again, as our Q-value function is learning over time and nGAE value could be soon obsolete. But this again can be solved by replay buffer technique described bellow.
Replay Buffer Recalculation
Simply done by having two layered Replay Buffer. One layer is Full Memory and second layer is optimized Fast Memory. When we query experience from replay buffer for self-play we doing it from fast memory, which is nothing else as classic implementation of replay buffer. However once a time, hyperparameter to be tuned, we query several episode from full memory, re-assign credit, and push to fast memory. Sizes of both full memory and fast memory is configurable to cover accurate enough approximation of n-step GAE, and benefit from more diverse Floating Step signal. Same time this approach allows to have multiple fast memory instances, and therefore different re-assign of credit approaches can be done per fast memory, which can allows separate learning experience algorithm, like HER, per algorithm as I described in BNPO blog post. Overall performance overhead depends on hyperparameters, but I found it works reasonable in my test with only 10% to 20% slowdown, however my tests are just for brief demonstration no full evaluation of this approach.
Importance Resampling
As I described briefly at B(N)PO post, Importance Resampling(IR) may play quite a role in B(N)PO, in particular in D(D)PG. However keeping up to date IR-ratio, ratio of how more probable is our new policy will come with experienced transition rather than the old policy, can be quite performance overkill. Imagine recalculating it every time per buffer sample, which is in fact for every self-play. There our Replay Buffer Recalculation, described above, can save the day. By our double layered memory buffers, we will keep recalculating ratio only few times (but for full episode!), but using it many more times. Actually same idea behind recalculation for HER algorithm. And as for keeping it up to date you need to tune hyperparameters like : memory_size, optim_pool_size, and optim_epochs. Memory size tells you how far to memory you want look, optim pool size will control life span of recalculated IR-ratio. As for code to reflect IR-ratio, you can check calculation of IR ratio and PER buffer utilization.
